|
Home Machine Tool Archive Machine-tools Sale & Wanted Société Genevoise d'Instruments de Physique Operation & Maintenance Manuals are available for most SIP Jig Borers SIP Home Hydroptic 6A & 7A Jig Borer 1-H Jig Borer 2P Tooling Cabinet Jig Borer 3K Jig Borer 4G Jig Borer 5E Jig Borer 8P Accessories Jig Borers 1920s 2C & No. 3 Other Early SIP Products |

|
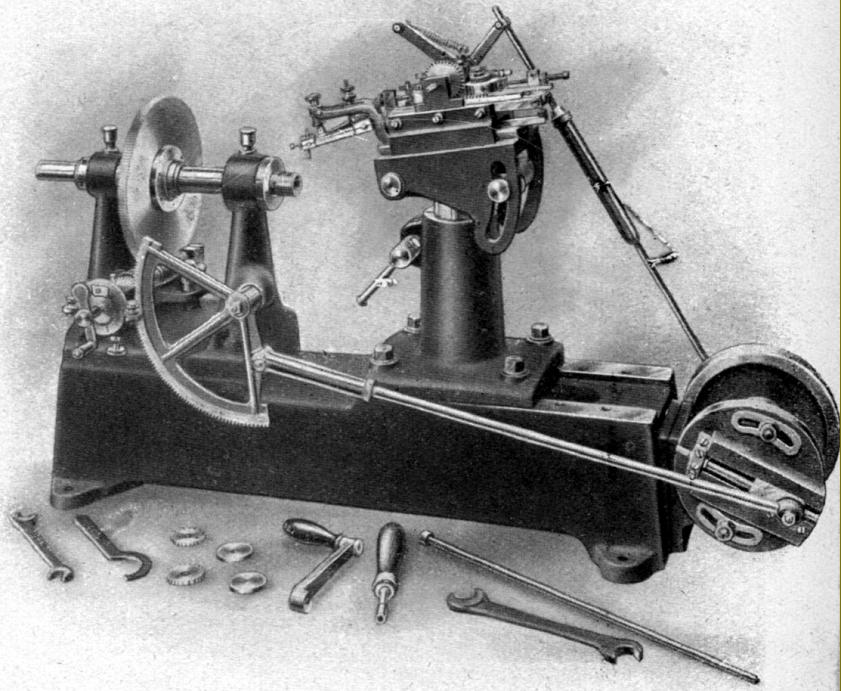
SSIP lathes are very rare, and few can have been made. This is the SIP No. 2 lathe 80 mm centre height and 200 mm between centres. Not an ordinary high-precision lathe, but one specially constructed for the automatic correction, checking and measuring very high quality screws, thread gauges and taps, etc. It was fitted with an automatic leadscrew corrector and equipment that allowed it to compensate for errors developed, for example, during hardening of the parts being tested.. Like that on an ordinary G.Boley precision lathe, the leadscrew ran down the centre line of the bed and was completely protected from the wearing effects of swarf and dirt. |

|
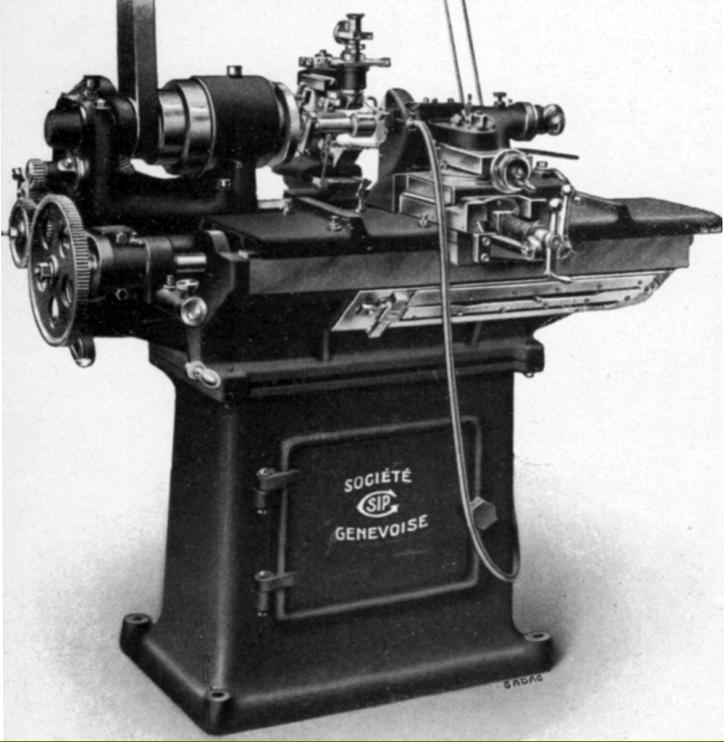
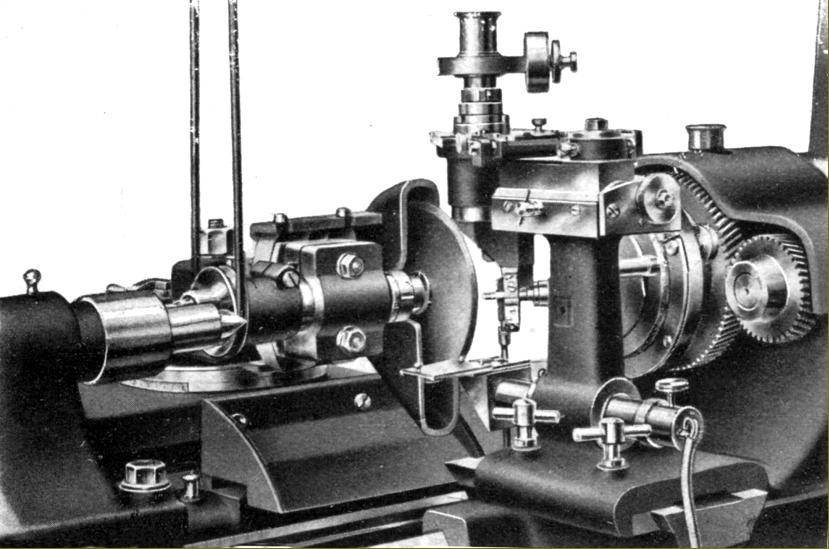
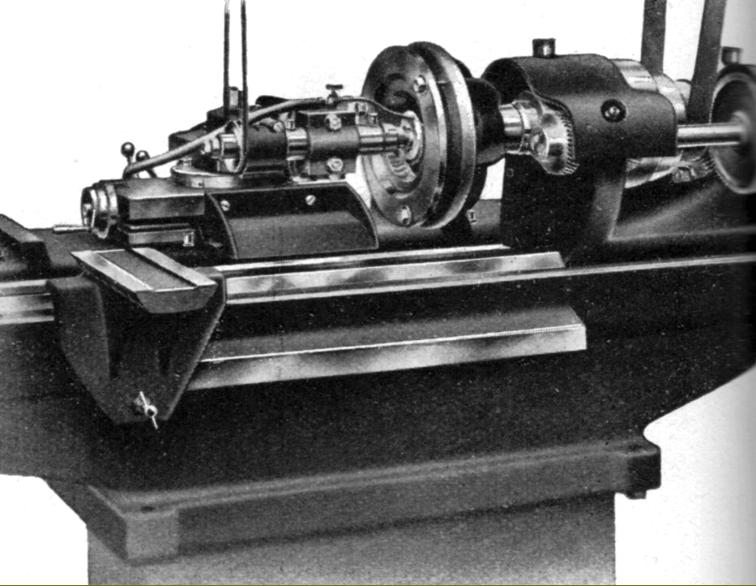
SIP No. TF4 special lathe with a 135 mm centre height and 400 mm between centres. A larger version, with a 155 mm centre height, was also listed. Like the Bryant Symons lathe, this SIP lathe had separate front and rear bed sections, the front carrying the carriage and the rear the tailstock. It may also have been fitted with an automatic forward/reverse mechanism to the carriage drive. |

|
|
||


|
The TF4 had separate front and rear bed sections, the front carrying the carriage and the rear the tailstock. It may also have been fitted with an automatic forward/reverse mechanism to the carriage drive. |
||





|
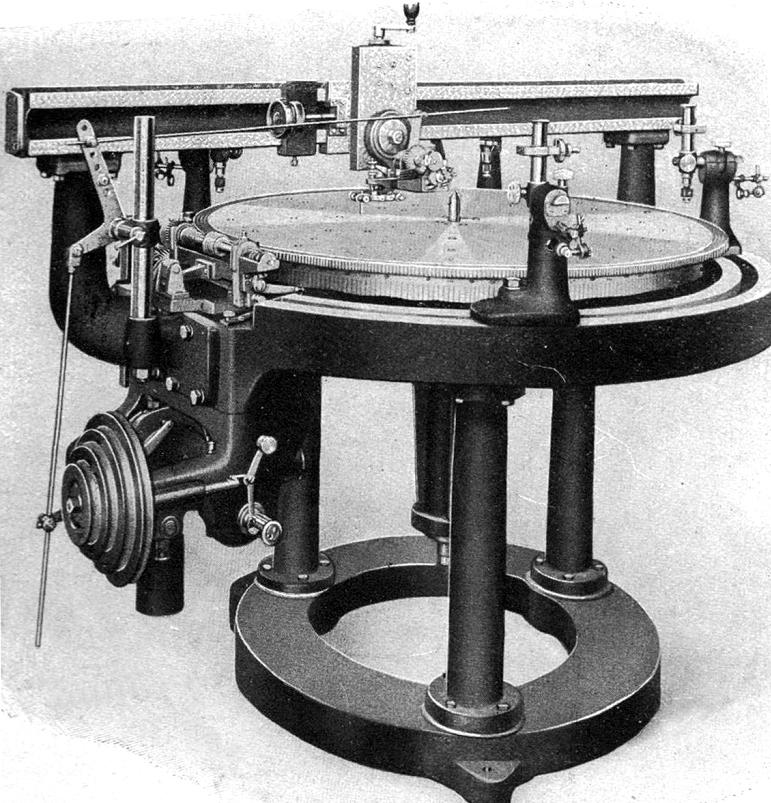
SIP high-precision "Universal Circular Dividing Machine" - fitted, as were all such circular and linear machines, with corrected leadscrews and worm-wheels. |
|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Jig Borer 3K Jig Borer 4G Jig Borer 5E Jig Borer 8P Accessories Jig Borers 1920s 2C & No. 3 Other Early SIP Products Société Genevoise d'Instruments de Physique Home Machine Tool Archive Machine-tools Sale & Wanted |
||